TEXTILE & FOOTWEAR

When engaged in sporting activity, or simply through our normal daily activities, perspiration is a natural phenomenon designed to regulate our body temperature. However, it can pose a challenge for our clothing and shoes, and can result in unpleasant smells. SANAFOR® actively fights these odors, which are caused by certain bacteria.
Click here for a case study to better understand where such unpleasant odors come from and how SANAFOR® contributes to keeping your clothes and shoes fresh, giving you a comfortable feeling all day long.


While carpets can create a warm and cozy feeling in our homes, they also easily capture dust and dirt, which are ideal sources of food for micro-organisms. Cleaning carpets, however, can be challenging.
With permanently integrated SANAFOR® protection, your carpets can keep their freshness, providing the feeling of comfort and well-being. SANAFOR® antimicrobial technology offers a durable protection, even after many wash or cleaning cycles. It will not impact any other properties of textiles or shoes, and it is safe when in contact with skin.

Case study: Odor control
With 2 to 4 million sweat glands in the human body and a maximum average production of 2 to 4 liters of sweat a day, our clothes and shoes are constantly challenged. But sweat by itself is nearly odorless, so where do unpleasant smells come from?
There are two kinds of sweat glands: eccrine, containing mainly water and some salts, and apocrine, which contain proteins in addition to water and salts. These proteins serve as nutrients for bacteria (e.g. Proteus vulgaris) which are present everywhere on skin, hair, clothes and other items, and the resulting volatile decomposition products create the unpleasant odors that we associate with perspiration. So, it’s the bacterial decomposition of sweat that creates the typical acrid odor.

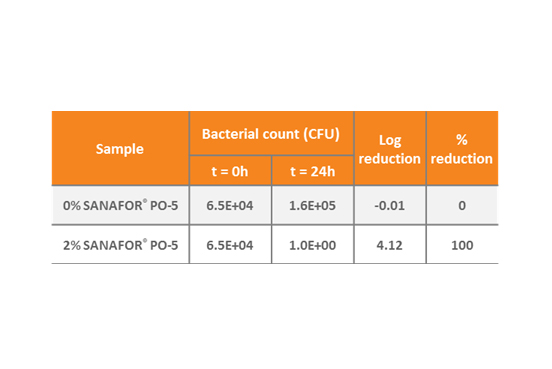
The ISO 22196 international standard test method for assessing antibacterial activity resulted in significant bacterial growth of Proteus vulgaris on untreated control samples, whereas the 2% SANAFOR® PO-5 treated samples exhibited a 100% reduction (> 4 log reduction after 24h contact time). The results are summarized in the adjacent table.